Jaundice - liver
disorder its cause and
management
Hello, today I am going to tell you about a very common disease known as jaundice after reading this article you will be able to tell its cause and its early management
Jaundice
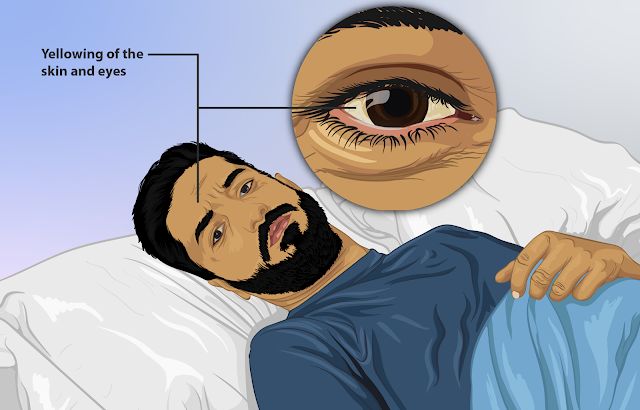
- It is a yellow discoloration of skin, mucus membrane and conjunctiva(it is a tissue that covers the sclera,sclera is a white portion of the eye)
- Main diagnosis is done by conducting a blood test for bilirubin
- Normal range of bilirubin- 0.5-1.5mg/dl
- In jaundice bilirubin is > 2.5mg/dl
- It is a yellow discoloration of skin, mucus membrane and conjunctiva(it is a tissue that covers the sclera,sclera is a white portion of the eye)
- Main diagnosis is done by conducting a blood test for bilirubin
- Normal range of bilirubin- 0.5-1.5mg/dl
- In jaundice bilirubin is > 2.5mg/dl
Fate of bilirubin
- Bilirubin is formed by the breakdown of rbc, rbc life span is 120 days after 120 days rbc are not functional to transport gases so they go to spleen for destruction.
- Spleen in known as the graveyard of rbc
- Hemoglobin breaks down into
- Haeme
- Globin
- Haeme gets converted into biliverdin then it is oxidized and is converted into bilirubin , it does not stay in spleen so it moves out into blood then liver has an enzyme known as GTE enzyme(Glucoronyl Transferase enzyme)
- This enzyme catches bilirubin and converts it into conjugated bilirubin.
- Conjugated bilirubin transfers through bill canaliculli - common hepatic duct- cystic duct- gall bladder- small intestine
- Small intestine bacteria convert conjugated bilirubin into stercobilin it gives characteristic color to stool.
- Some conjugated bilirubin goes back to blood, then to the kidney from kidney it is excreted out as urobillinogen.
- It gives a dark color to urine.
- Bilirubin is formed by the breakdown of rbc, rbc life span is 120 days after 120 days rbc are not functional to transport gases so they go to spleen for destruction.
- Spleen in known as the graveyard of rbc
- Hemoglobin breaks down into
- Haeme
- Globin
- Haeme gets converted into biliverdin then it is oxidized and is converted into bilirubin , it does not stay in spleen so it moves out into blood then liver has an enzyme known as GTE enzyme(Glucoronyl Transferase enzyme)
- This enzyme catches bilirubin and converts it into conjugated bilirubin.
- Conjugated bilirubin transfers through bill canaliculli - common hepatic duct- cystic duct- gall bladder- small intestine
- Small intestine bacteria convert conjugated bilirubin into stercobilin it gives characteristic color to stool.
- Some conjugated bilirubin goes back to blood, then to the kidney from kidney it is excreted out as urobillinogen.
- It gives a dark color to urine.
Symptoms of jaundice
- Dark urine - due to more urobillinogen
- Pale stool or white stool
- Fever with rigors
- Dry eyes, dry mouth,
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Malaise
- Weakness
- Stomach pain before and after food
- Itching without eruption
Classification of jaundice
- Dark urine - due to more urobillinogen
- Pale stool or white stool
- Fever with rigors
- Dry eyes, dry mouth,
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Malaise
- Weakness
- Stomach pain before and after food
- Itching without eruption
Pre hepatic
Hepatocellular
Post hepatic
Pre hepatic
- Spleen produces more bilirubin due to haemolysis
- It is normally congenital or due to mismatched blood transfusion
- Gilbert syndrome - it is a non hemolytic hyperbilirubinaemia
- In this there is an autosomal dominant mutation this reduces expression of uridine 5 - diphospho-glucoronyl transferase
- This increases unconjugated bilirubin in the blood
- It has a good prognosis it does not require any treatment
Various reasons
- cancer outside liver either in the ampulla or bile duct
- choledocholithiasis (bile duct stones)
- Stomach warms
- Strictures
Hepatocellular
- In hepatocellular, problem lies in the liver
- There is an injury to liver cells
- Liver cells are unable to transport conjugated bilirubin to bile duct it mostly happens due to parenchymal layer disease
- Hepatocytes impairment and swelling of cells also causes this
- Due to the swelling of cells concentration of both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin in the blood increases this happens because bilirubin transport is disturbed.
- GTE enzyme does not work properly
Post hepatic
Causes
- Hepatocytes are not able to initiate bile flow
- Obstruction of bile ducts or portal ducts
- Obstruction of bile flow in portal hepatitis and ampulla
- Without treatment, it becomes worse as conjugated bilirubin increases in blood so surgical or endoscopic corrections are needed
Diagnosis of jaundice
- Various enzymes are checked
- ALT/AST - aminotransferases and alkaline phosphatase
- Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase
- Prothrombin time
Pre hepatic
- Bilirubin is normal Or slightly increased
- Conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin -normal
Hepatic
- Bilirubin, conjugated bilirubin and unconjugated bilirubin increased
- SGOT/ALT increases
Post hepatic
- Serum bilirubin and conjugated bilirubin increases
- Unconjugated bilirubin normal
- Liver function test is abnormal
- ERCP(endoscopic resonance cholangiopancreatography and MRCP(Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) is done before surgery
- These techniques produces detail images of pancreas and bile ducts
Management of jaundice
- If only GGT is increased - proper diet and exercises will help
- - Avoid alcohol
- Increased ALP or abnormal LFT -liver biopsy
- Treat the cause and subside the disease is the main management
Hope this article has helped you in some way if you have any queries you can contact me through my contact details
Thank you
https://dreamunlocker.blogspot.com/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IJkoa67Z6Y8
DISCLAIMER- All the information on this website is published in good faith and for general information purpose, only http://dreamunlocker.blogspot.com does not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability, and accuracy of this information. Any action you take upon the information you find on this website (http://dreamunlocker.blogspot.com), is strictly at your own risk. http://dreamunlocker.blogspot.com will not be liable for any losses and/or damages in connection with the use of our website.





2 Comments
Great post! Very informative about Jaundice. There are some medial terms which I didn't understand, but I really like reading this article. Thank you for sharing your knowledge on these kinds of topics.
ReplyDeleteThnku so much and if you want to know about any term feel free to ask..
Deleteplease dont enter any spam link in the comment box